Building Construction
The Chemical Engineering building is located on the East side
of the new NTUA campus, facing Mountain Hymettus on one side and
the main campus square on the other, from which pedestrian access
is mostly obtained at different levels. It has a total covered surface
of approximately 30,000m2, and is composed of units of various sizes
and uses organised around medium sized courtyards. The main axis
of the building runs North to South and is accentuated by two 6m
wide corridors on each side of the courtyards which were supposed
to form interior streets linking various campus buildings and services
together.
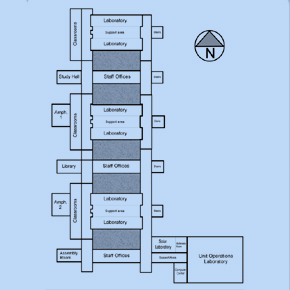
The building can be divided into three equivalent parts, each formed
of one laboratory unit on the North side and one office unit on
the South side of a courtyard, joined by teaching, research and
administration spaces on the East and west sides. The building is
constructed of reinforced concrete with brick infills. It has no
insulation and windows are single-glazed.
 |
   |
|
Heating / Ventilation / Cooling and Lighting System
? Heating system: Three boiler rooms (one per section) Fuel: oil
? Ventilation: Natural ventilation
? Cooling: Local split type heat pumps (for offices and laboratories)
? Lighting: Fluorescent, centrally or locally controlled (~17W/m2)
Problems / Damages
The building was designed in the 1960's, but was only occupied
a few years ago. It then became obvious to users that the original
design was not appropriate for a University building of this type,
since common spaces were too generous, occupying more than 70%
of the total covered spaces of the building. Apart from the feeling
of many users that much of this space is wasted, while many of
their ever-growing requirements are not sheltered adequately,
there are problems with heating and natural lighting of the common
spaces which are mostly dark and cold, giving a derelict feeling
to the whole building. Besides the above, the lower levels of
the two main corridors were left open, forming pilotis -a popular
scheme in the architecture of the 1960's, nowadays resulted to
uncomfortable spaces, exposed to strong winds and rain during
most of the school season.
|